Zooplankton of Southern California
Photographed and compiled by Peter J. Bryant (pjbryant@uci.edu)
Department of Developmental and Cell Biology, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697
Ciliates

Parafavella sp.

Stalked Ciliate,
Peritricha sp.

Tintinnid

Bell Tintinnid,
Tintinnopsis (campanula?)

Vorticella sp.

Globigerina sp.

Radiolarians

Diploconus sp.

Acantharia sp.

Unidentified 1

Unidentified 2

Rotifers

Parenchymella larva

Coronate larva

Cyphonautes larva

Bougainvillia sp.

Cladonema (californicum?)

Corymorpha bigelowi
a.jpg)
Giant Bell Jelly,
Scrippsia pacifica
a.jpg)
Crystal Jelly, Aequorea victoria

Clytia elsaeoswaldae

Clytia gracilis

Clytia sp.

Obelia sp.

Lensia campanella

Siphonophore,
Nanomia sp. (larva)

Unidentified Narcomedusa

Liriope tetraphylla
Actinostolidae

Onion anemone,
Paranthus rapiformis

Tube-dwelling anemone, Isarachnanthus nocturnus (Cerinula larva)

West Coast Sea Nettle,
Chrysaora fuscescens

Moon Jelly,
Aurelia aurita

Trematode (Cercaria Larva)

Sea gooseberry,
Pleurobrachia bachei

Owenia sp. (larva)

Unidentified larva

Sternaspis sp.

Fireworm,
Odontosyllis phosphorea

Unidentified polychaete larva #1

Unidentified polychaete larva #2

Unidentified polychaete larva #3

Unidentified polychaete larva A3

Unidentified polychaete larva A4

Brown-streak Stiliger,
Stiliger fuscovittatus

Sea Snail,
Atlanta (californiensis?)

Sea Butterfly,
Desmopterus pacificus
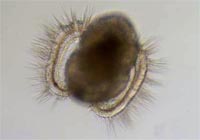
Veliger larva

Veliger larva

Limpet Veliger

Amphithoe plumulosa

Skeleton Shrimp, Caprella mendax

Elasmopus bampo

Jassa slatteryi

Zeuxo sp.

Hyalid amphipod

Goose Barnacle,
Pollicipes polymerus

Ivory Barnacle,
Amphibalanus eburneus

Marine Cladoceran,
Evadne sp.
Marine Cladoceran,
Penilia avirostris

Marine Cladoceran, Pleopis polyphemoides

Marine Cladoceran,
Pseudevadne tergestina

Calanoid Copepod,
Acartia sp.

Calanus pacificus

Sea Louse,
Caligus sp.

Caligoid (parasitic) copepod
(Sea Louse)

Mecynocera clausi

Paracalanus parvus

Calanoid copepod

Cyclopoid Copepod

Cyclopoid Copepod

Harpacticoid Copepod

Nauplius II larva

Cumacean

Water slater,
Asellus aquaticus

Marine isopod, Cilicaea sp.

Harford's Isopod,
Cirolana harfordi

Elthusa californica

Excirolana chiltoni

Bigtail Isopod,
Exosphaeroma amplicauda

Exosphaeroma inornata

Paranthura elegans

Marine Isopod, Zeuxo sp.

Marine Isopod

Marine Isopod

Opossum Shrimp

Ostracod

California Spiny Lobster,
Panulirus interruptus, larva

Striped shore crab,
Pachygrapsus crassipes, zoea larva

Striped shore crab,
Pachygrapsus crassipes, megalops larva

Zoea Larva

Zoea Larva

Swimming Crab,
Portunus xantusii, megalops larva

Yellow Shore Crab,
Hemigrapsus oregonensis

A collection of unidentied megalops larvae

Rosy Bryozoan, Integripelta bilabiata, Coronate larva

Cyphonautes larva (unidentified)

Larva of unidentified Brittle Star

Brachiolaria larva of unidentified Sea Star

Juvenile Sea Star
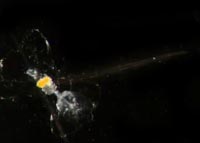
Fritillaria borealis

Oikopleura sp.

Pyrosome,
Pyrosoma sp.
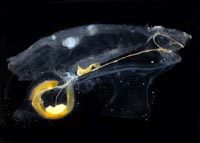
Salp,
Cyclosalpa affinis

Salp,
Salpa fusiformis
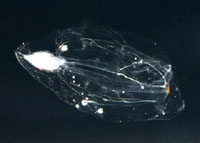
Salp,
Thalia rhomboides

